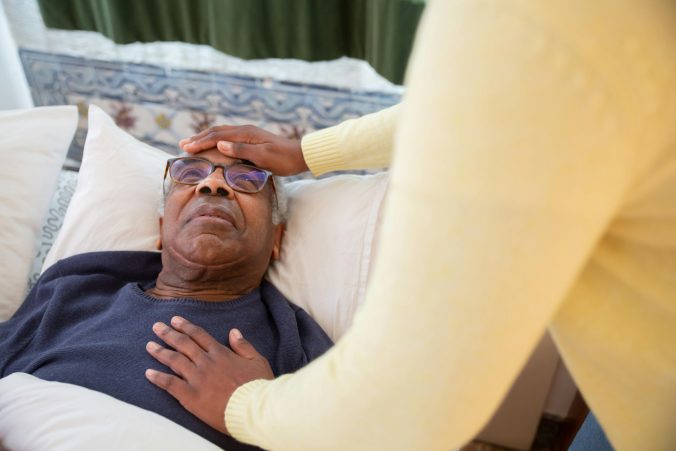
In palliative care of seriously ill and dying patients, healthcare professionals deal not only with medical needs, but also with the existential needs of patients and their families. Although the palliative healthcare teams can receive support from professions that focus on existential conversations, it is the physicians and not least the nurses, care assistants, physiotherapists and occupational therapists who more continuously talk with patients about life, dying and death. Sometimes the conversations are planned in advance, but often they arise spontaneously in connection with the care interventions.
A Swedish interview study investigated experiences of spontaneous existential conversations with patients and their families within the healthcare professions that meet them daily: nurses, care assistants, physiotherapists and occupational therapists. They were asked questions about when existential conversations could arise and what influenced the quality of the conversations. They were also asked about how they talked to patients about their thoughts about death, how they reacted to patients’ existential questions, and how they reacted when relatives had difficulty accepting the situation.
The aim of the study was to create a structured overview of the experiences of the healthcare professionals, a model of what was considered important for existential conversations to arise and function well. Strategies used by the palliative teams were identified, as well as obstacles to meaningful existential conversations.
The main concern for the healthcare professionals was to establish a trusting relationship with patients and next of kin. Without such a relationship, no meaningful conversations about life, dying and death could arise. A core category that emerged from the interview material was to maintain presence: to be like a stable rock under all circumstances. In the meeting with patients and relatives, they stayed physically close and were calmly present during quiet moments. This low-key presence could spark conversations about the end of life, about memories, about support for quality of life, even in situations where patients and relatives were afraid or upset. By maintaining a calm presence, it was perceived that one became receptive to existential conversations.
The palliative teams tried to initiate conversations about death early. As soon as patients entered the ward, open-ended questions were asked about how they were feeling. The patients’ thoughts about the future, their hopes and fears were carefully probed. Here, the main thing is to listen attentively. Another strategy was to capture wishes and needs by talking about memories or informing about the diagnosis and how symptoms can be alleviated. The healthcare professionals must also guide relatives, who may be anxious, angry and frustrated. Here, it is important not to take any criticism and threats personally, to calmly acknowledge their concerns and inform about possible future scenarios. Relatives may also need information on how they can help care for the patient, as well as support to say goodbye peacefully when the patient has died. Something that also emerged in the interviews was the importance of maintaining one’s professional role in the team. For example, a physiotherapist must maintain focus on the task of getting patients, who may lack motivation, to get up and exercise. A strategy for dealing with similar difficulties was to seek support from others in the care team, to talk about challenges that one otherwise felt alone with.
Something that could hinder existential conversations was the fear of making mistakes: then one dares neither to ask nor to listen. Another obstacle could be anxious relatives: if relatives are frustrated and disagreeing, this can hinder existential conversations that help them say goodbye and let the patient die peacefully. A third obstacle was lack of time and feeling strained: sometimes the health care professionals have other work tasks and do not have time to stop and talk. And if relatives do not accept that the patient is dying, but demand that the patient be moved to receive effective hospital care, the tension can hinder existential conversations. Finally, lack of continuous training and education in conducting existential conversations was perceived as an obstacle, as was lack of support from colleagues and from the healthcare organization.
Hopefully, the article can motivate educational efforts within palliative care for those professions that manage the existential needs of patients and relatives on a daily basis. You can find the article here: Interdisciplinary strategies for establishing a trusting relation as a pre-requisite for existential conversations in palliative care: a grounded theory study.

Written by…
Pär Segerdahl, Associate Professor at the Centre for Research Ethics & Bioethics and editor of the Ethics Blog.
Lagerin, A., Melin-Johansson, C., Holmberg, B. et al. Interdisciplinary strategies for establishing a trusting relation as a pre-requisite for existential conversations in palliative care: a grounded theory study. BMC Palliative Care 24, 47 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12904-025-01681-x
We recommend readings